Sponsored Content
European Union's Space Program Contributes to UNOOSA's "Space2030" Agenda
The United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs and the European Union Agency for the Space Programme have joined forces to unveil a groundbreaking report aiming to shed light on the crucial role played by the European Union in advancing the objectives of the "Space2030" Agenda and addressing long-term sustainable development concerns facing humanity.
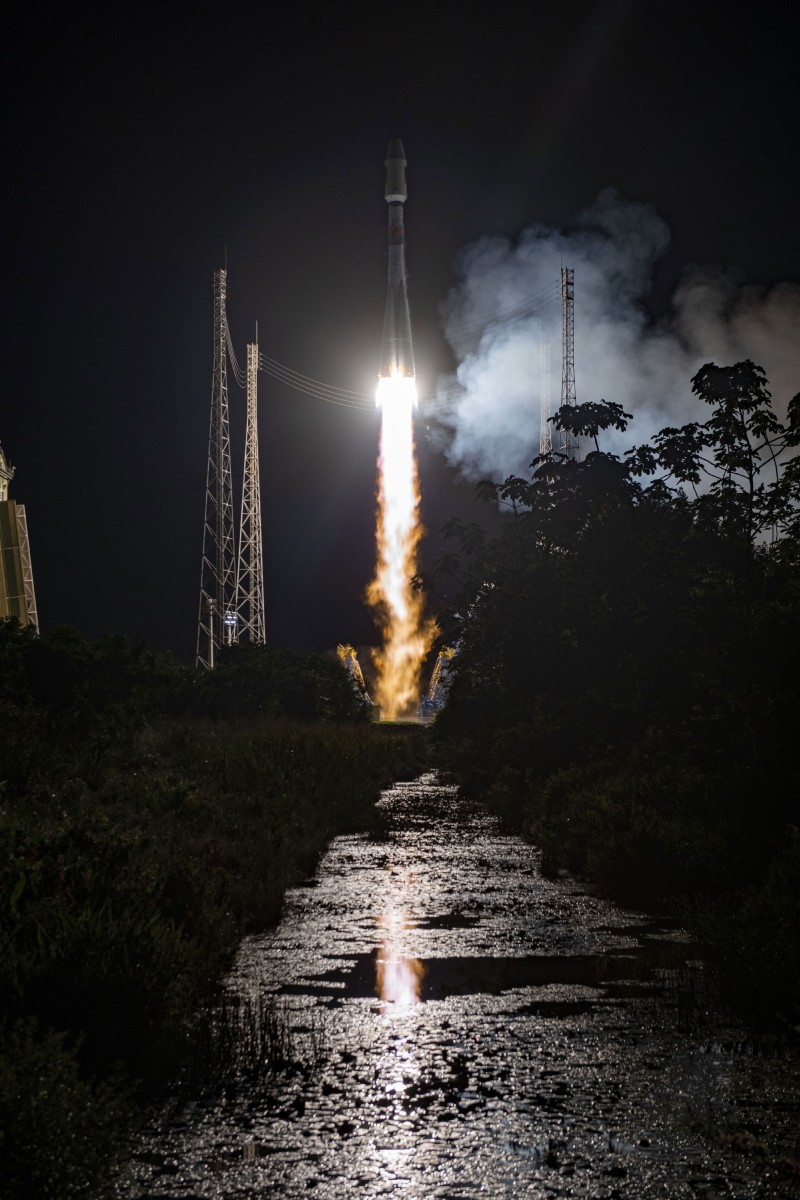 Overall, this report highlights the significant role of the European Union Space Programme and its components in addressing the challenges posed by a rapidly growing global population and advancing sustainable development goals. / Picture: © EUSPA - European Agency for the Space Programme
Overall, this report highlights the significant role of the European Union Space Programme and its components in addressing the challenges posed by a rapidly growing global population and advancing sustainable development goals. / Picture: © EUSPA - European Agency for the Space Programme
The comprehensive report focuses on highlighting the immense value of key components within the EU Space Programme, including Copernicus, Galileo, EGNOS, and GOVSATCOM. These components offer innovative and practical solutions to global challenges, providing a…
or Log In
Fast News Search